Juvenile Diabetes
CHILDHOOD CHRONIC DISEASE: Juvenile Diabetes (Type 1 Diabetes)
“Juvenile diabetes is a chronic disease affecting 1.5 million people, damaging tissues and organs systems leading to 18-years of shortened life expectancy and is expected to more than double over the next 15-years. While only 1% of patients achieve normal metabolic health, nutrition is both the problem and the solution as removing high-carbohydrate, often ultra-processed foods can lead to rapid normalization of glucose and reduced insulin within days.”
INCIDENCE:
Chronic diseases represent one of the foremost challenges to public health in the United States, and among these, diabetes stands as a critical crisis, particularly for our most vulnerable population—children. Juvenile diabetes is an escalating burden that is not only alarming and unsustainable but also undermines the immediate health of young patients and portends lifelong complications that reverberate through families, communities, and our healthcare systems. Over 800 million people live with diabetes1 and most recent U.S. estimates demonstrating that disease rates in the United States have risen from 11% to 14% over the last decade,2 with 1.5 million children burdened with juvenile diabetes, with incidence expected to double in less than 15 years.3-5 Less than 1% of children living with juvenile diabetes achieve normal glucose control (<5.7% HbA1c)6 in large part due to poor disease management strategies and improper nutritional management.7
DISEASE BURDEN:
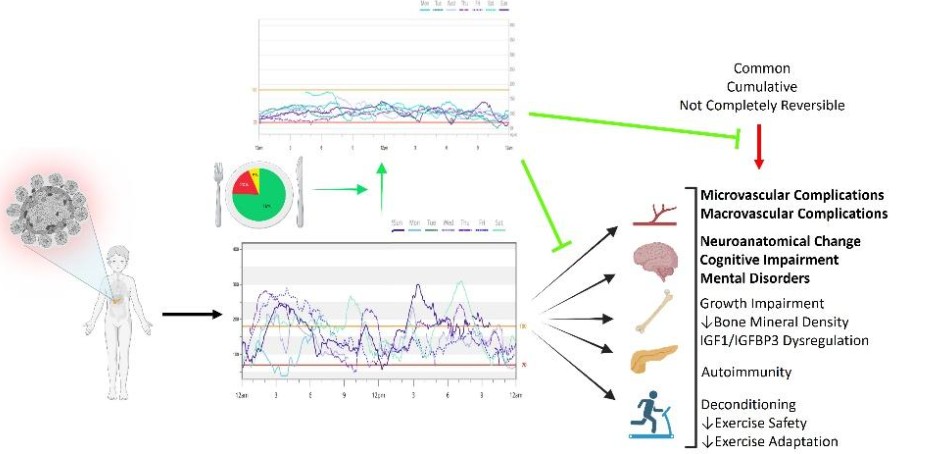
Juvenile diabetes leads to rapid changes in children’s brain neuroanatomy (within 3 years),8,9 impairing neurological development,8,9 leading to population-wide reductions across multiple metrics of cognitive function,10,11 ten-fold higher prevalence of anxiety and depression12,13, and more than double the rates of early child suicide.14 These vulnerable children also experience early atherosclerotic progression (within 4 years),15 leading to a 10x higher risk for cardiovascular disease.16-18 Consequently, juvenile diabetes increases the risk of acute and chronic complications19-33, all-cause mortality,22,23,25,34 with life expectancy shortened by over a two decade (18 years).3,22,25,35 The of acute and chronic medical complications 34,36-41 of juvenile diabetes are common and have a long-term legacy effect (cumulative and not fully reversible) on health and survival if effective therapeutic interventions are not rapidly implemented.37,42-45
THERAPEUTIC GAPS:
While technological advancements, increased technology use, and stricter glycemic guidelines have been observed over the last decade, data from 81 U.S.-based endocrinology practices in 35 states has reported worsened juvenile diabetes control6,46 with 99% of patients currently living with metabolic dysfunction.6,47,48 Even next-generation technology does not reliably improve disease outcomes (HbA1c) by more than 1% or reliably achievestandard of care disease targets.49-53 almost entirely explained by poor nutritional guidance and management.

The over-insulination of patients with juvenile diabetes leads to lifelong insulin resistance and an accelerated rate of obesity, which now outpaces the general population.54,55
RAPID NORMALIZED GLUCOSE & REDUCED INSULIN:
Recent data from Koutnik et al., from over 100 studies and 46,000 patients with juvenile diabetes,56,57 largest analysis of nutrition’s impact on juvenile diabetes, demonstrated that high carbohydrate diets make normal glucose and reduced insulin unachievable, while reductions in highly processed carbohydrates resulted in dose-depending improvements in diabetes management. Critically, over >75% of published data in patients undergoing therapeutic carbohydrate reduction achieved normal glucose (<5.7% HbA1c) without adverse outcomes, an achievement not possible with any other medicinal or technological approach to diabetes management.
A recent analysis from Harvard and Duke medical schools support this data, demonstrating that 42% of both children and adults with diabetes were able to achieve normal glucose control and very low insulin requirements utilizing this approach.

Remarkably, optimizing healthy nutritional delivery to patients with juvenile diabetes technology alongside diabetes technology offers the opportunity to automate normal glucose control and significantly reduced insulin requirements in days as examples below of over 200 children who were all able to achieve normal metabolic health through therapeutic carbohydrate reduction. Demonstrating rapid remission in juvenile diabetes by removing high carbohydrate and ultra-processed food. This represents a major governmental opportunity to demonstrate direct impact on the most vulnerable populations (children) with chronic disease.
SAFETY & FEASIBILITY:
Institutional international guidelines have been developed by endocrinologists, diabetes, certified diabetes educators, and researchers providing safe healthcare guidance for normal glucose control and rapid reductions in insulin.56 An international survey of almost 1000 patients and caregivers of those affected by juvenile diabetes demonstrates that food has a major impact on their disease management. Data from Koutnik et al.,56,57 also show no elevated incidence of adverse outcomes utilizing therapeutic nutrition strategies which reduce high carbohydrate intake. The longest longitudinal report of juvenile diabetes implementing a therapeutic carbohydrate reduction utilizing a ketogenic diet over 10 years demonstrates remarkable therapeutic potential with adverse events.47,48
CALL TO ACTION: The mounting evidence clearly demonstrates that juvenile diabetes is a multifaceted public health crisis—one that imperils the cognitive, cardiovascular, and overall health of our children. The current management strategies, heavily reliant on over-insulination of children and inadequate nutritional management, have proven inadequate to reverse or even adequately slow disease progression. In light of this, it is imperative that healthcare providers, researchers, and policymakers urgently adopt and promote comprehensive therapeutic interventions that prioritize nutritional optimization.
By harnessing the power of therapeutic carbohydrate reduction, we stand at the threshold of a transformative shift in diabetes care—one that promises to restore health, extend life expectancy, and improve the quality of life for millions of children. This is not merely a clinical imperative but a moral one: to protect our children from the ravages of a disease that too often dooms them to a lifetime of suffering. As stewards of public health, we must mobilize our resources, revise our treatment paradigms, and work collaboratively to ensure that every child with juvenile diabetes has the opportunity to achieve normal metabolic health and lead a healthier, more fulfilling life.
Picture of children with Juvenile Diabetes who have normal metabolic health (<5.7% HbA1c), dramatically reduced insulin requirements, and high quality of life through Therapeutic Carbohydrate Reduction.


Andrew Koutnik, PhD, is an award‑winning Research Scientist and globally recognized authority on metabolic health, diabetes management, and human performance optimization, having collaborated with leading institutions such as NASA, John Hopkins, Harvard Medical School, and the Department of Defense, amongst others. Dr. Koutnik was diagnosed with Obesity and Juvenile Diabetes in adolescence and has investigated lifestyle intervention to prevent and eliminate chronic disease burden.